hot/cold
the science of contrast therapy
The Power of Contrast Therapy
Alternating between hot and cold exposure, commonly known as contrast therapy, has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various ailments. From saunas and cold plunges to modern cryotherapy, this practice leverages the body’s physiological response to temperature changes to promote healing, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation. The benefits of contrast therapy are not just anecdotal—scientific studies have begun to reveal the mechanisms behind its effectiveness.1 2 3

heat: Vasodilation and Relaxation
When exposed to heat, blood vessels expand in a process called vasodilation. This increased blood flow delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues, supporting repair and reducing soreness. Heat exposure also promotes relaxation by lowering cortisol levels and stimulating endorphin release, which can help reduce stress and improve mood.1 2 In saunas, this effect is amplified by the gradual warming of the body, creating a deeply restorative experience.

cold: Vasoconstriction and Recovery
Cold exposure, on the other hand, triggers vasoconstriction, where blood vessels narrow to conserve heat. This process reduces inflammation and swelling by limiting fluid accumulation in tissues. Cold also numbs nerve endings, providing temporary pain relief. After the cold exposure, the body naturally warms up, stimulating circulation and creating a sense of invigoration.

The Synergy of Hot and Cold
The alternation between hot and cold exposure creates a powerful circulatory workout. Heat opens blood vessels, flushing out toxins and delivering nutrients, while cold constricts them, helping to reduce inflammation and promote recovery.1 This dynamic process enhances lymphatic drainage and improves overall cardiovascular health.

Immune System Activation
Emerging research suggests that alternating temperature exposure may also boost immune function. Heat exposure increases the production of white blood cells, while cold exposure stimulates norepinephrine release, which has been linked to reduced inflammation and enhanced immune response.1 2 Together, these effects may help the body fend off infections and maintain overall health.
Practical Tips for Hot and Cold Therapy
Incorporating contrast therapy into your routine doesn’t require expensive equipment. A sauna session followed by a cold shower, or alternating between a hot tub and a cold plunge, can yield significant benefits. Start with shorter exposures—10–15 minutes of heat followed by 1–3 minutes of cold—and gradually build up as your body adapts. Always listen to your body, and consult a healthcare provider if you have underlying health conditions.

A Natural, evidence-Backed Practice
Contrast therapy is a simple yet powerful practice with roots in ancient traditions and growing support from modern science. By harnessing the body’s natural responses to heat and cold, this therapy offers a holistic approach to recovery, stress reduction, and overall wellness. Whether for relaxation or performance, alternating hot and cold exposure can be a transformative addition to your health routine.
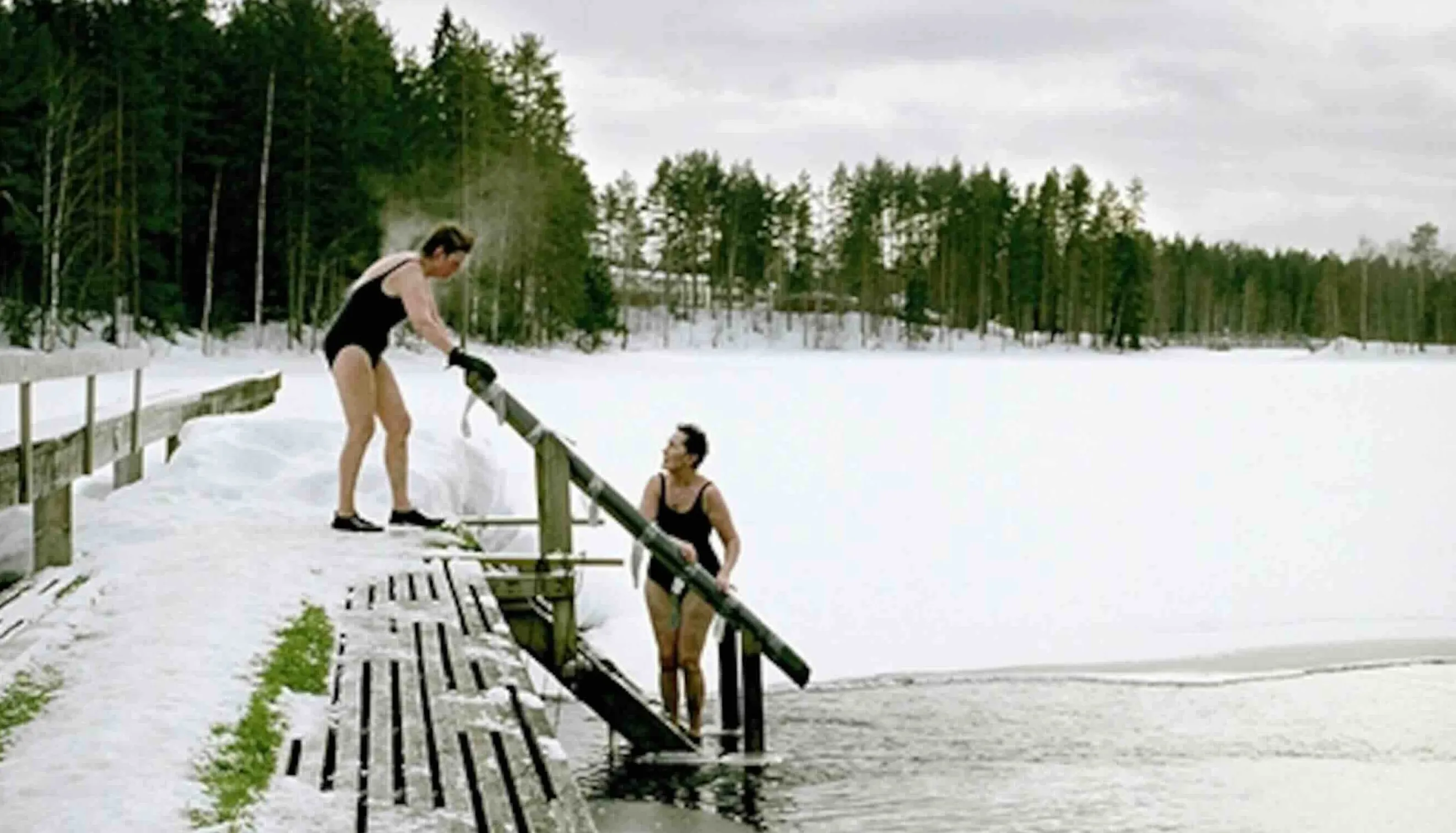

see for yourself
Ready to experience the timeless tradition of sauna for yourself? Step away from the everyday and immerse yourself in a world of heat, steam, and relaxation. Book your free session at our sauna and discover the profound joy of connection, renewal, and wellness firsthand.
